The Power of Health Assets
Research shows that people have a better opportunity for health when they have particular health assets available. One of the most empowering things we can do to support community health improvement is to help vulnerable populations strengthen their health assets. Community Health Solutions developed The Health Asset Model to inform and guide this work.
The Health Asset Model
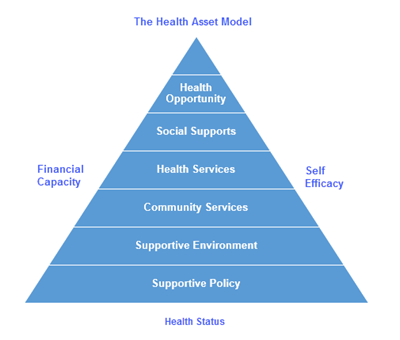 The Health Asset Model is an evidence-based framework for improving health opportunity for individuals and populations. As illustrated in the graphic, the model defines the types of services and supports that are necessary to enable health opportunity. Key concepts include:
The Health Asset Model is an evidence-based framework for improving health opportunity for individuals and populations. As illustrated in the graphic, the model defines the types of services and supports that are necessary to enable health opportunity. Key concepts include:
- Health Opportunity. Health opportunity can be defined as the ability of individuals and populations to pursue their goals for health and well being. Health opportunity is enabled by the health assets outlined in the model.
- Moderating Factors. Health opportunity is moderated by a person’s underlying health status, financial capacity for pursuing health, and self efficacy (motivation, knowledge, and skills) for pursuing health. Health assets can be used to help people address challenges related to these moderating factors.
- Social Supports. Social supports can be defined as personal and community relationships that support health and well being. Social supports are often overlooked as a key health asset.
- Clinical Services. Clinical services include the array of clinical health services that may be necessary for preventing and treating disease and disability. These include medical care, oral health care, behavioral health care, clinical case management, and other clinical health care services.
- Community Services. Community services include the array of enabling services that may be necessary for sustaining health and accessing health care services. Examples include education, transportation, housing, nutrition, recreation, financial assistance, job training, and community financial services.
- Supportive Environment. A supportive environment is an environment that supports health and well being. Environment settings include the home, the neighborhood, the workplace, and the school. Environment factors include the safety of air, water, food, and structures, as well as social, economic, and cultural factors that influence health and well being.
- Supportive Policy. Supportive policy is essential for enabling a supportive environment as well as access to services. Supportive policy is important not only in the realms of public health and health care, but also in education, transportation, housing, social services, community financial services, community development, and economic development.
Community Applications
The Health Asset Model can be applied for any community population, including children, adults, seniors, and populations with particular health risks, health conditions, or disabilities. It can also be applied for populations in particular settings and places such as schools, workplaces, and neighborhoods. Ideally this work is conducted collaboratively to optimize collective impact. The model can be applied using the following process.
- Define the population.
- Identify health needs and goals.
- Identify health assets and gaps based on the The Health Asset Model.
- Address health asset gaps by connecting population members to appropriate services and supports.
- Strengthen community health assets (services, environments, and policies) where needed.
- Refine and improve the initiative in response to feedback.
- Continue working to sustain access to community health assets through innovative service models, funding models, and policies.
Community Health Solutions provides research, consulting, and learning supports for applying the Community Health Asset Model. Please contact us to learn more.

